In today’s fast-paced technological world, energy efficiency and smart control are no longer luxuries but rather have become necessities. That is the point where one must consider Power Electronics: Key Concepts and Applications. Any time you change your smartphone, drive an electric vehicle, or draw renewable energy into your home, electrical works quietly in the background, controlling and efficiently converting electrical energy.
What is Power Electronics?
Electronics is a sub-division of electrical engineering that uses solid state to convert, control, and condition electric energy, serving as an intermediate link between energy systems and control systems.
At the heart of essentials and such a vast field called power electronics stand conversion activities:
• AC-to-DC conversion or rectification
• DC-to-AC conversion or inversion
• DC chopping
• AC-to-AC conversion
The
devices are diodes, transistors, MOSFETS, IGBTs and thyristors acting like a
switch for controlling the current flow.
🔍 Key Concepts in Power Electronics
1. Devices that Alter Supply
A great deal of power electronics circuits utilize semiconductor devices, such as:
• Diodes – conduct in one direction only.
• MOSFETs – for the switching function, great for low to moderate input.
• IGBTs – for high input voltage and current.
• SCRs – mainly suitable for high applications.
2. Converters
The building blocks for power electronics are:
• Rectifiers (convert AC voltage into DC)
• Inverters (convert DC voltage into AC)
• DC-DC converters to voltage
• AC-AC converters to change voltage and frequency of AC signals
3. Control Techniques
Feedback and control loops are often unavoidable for systems to achieve stability, efficiency, and safety. Commonly used methods are:
• Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
• Voltage and current regulation
• Closed-loop
control systems
Applications of Power Electronics
It's amazing what electronics can do behind the scenes:
🔋 Renewable energy systems
• Solar inverters convert DC from panels to A.C.
• Wind turbines employ converters for grid synchronization.
🚗 Electric Vehicles (EVs)
• Motor drives, battery charging, and management all depend on electronics.
🏠 Consumer Electric
• Power supplies from laptops to LED lightings are being designed with efficiency in mind, minimizing energy consumption and heat generation.
🏭 Industrial Automation
• VFDs that depend on variable frequencies help control the speed with which motors would be running; they also help in getting maximum efficiency.
⚡ Power Grids
• By integrating smart-grid converters and energy storage systems, factor correction becomes more reliable and more efficient.
Why It Matters
With world-wide interest in energy efficiency, renewables, and electrification, electric comes as a critical enabler of sustainable systems while keeping them compact, energy-efficient, and reliable.
Final Thoughts
While power electronics may be invisible to the layman, it serves as the backbone for everything modern. Technologies will evolve, as this field also will; hence the time draw nearer for cleaner and smarter energy development. Whether you are a student, a professional engineer, or a curious person, power electric will take you to a whole new universe where science meets social sustainability, and innovation creates progress.

 Applications of Power Electronics in Renewable Energy Systems
Applications of Power Electronics in Renewable Energy Systems  Designing Efficient Power Converters: Tips and Techniques
Designing Efficient Power Converters: Tips and Techniques  Advances in Power Semiconductor Devices
Advances in Power Semiconductor Devices  Cybersecurity in Power Systems: Protecting Critical Infrastructure
Cybersecurity in Power Systems: Protecting Critical Infrastructure  The Evolution of Power Transmission: From AC to HVDC
The Evolution of Power Transmission: From AC to HVDC  Impact of Energy Storage on Power System Management
Impact of Energy Storage on Power System Management  Load Flow Analysis : Techniques and Applications in Power Systems
Load Flow Analysis : Techniques and Applications in Power Systems  Microgrids: Enhancing Resilience and Efficiency in Power Systems
Microgrids: Enhancing Resilience and Efficiency in Power Systems  Innovative Technologies in Power System Protection
Innovative Technologies in Power System Protection  Challenges and Solutions in Power System Stability
Challenges and Solutions in Power System Stability  Final Year Electrical Engineering Project Ideas for College Students
Final Year Electrical Engineering Project Ideas for College Students  The Role of Renewable Energy in Modern Power Systems
The Role of Renewable Energy in Modern Power Systems  Smart Grids: Revolutionizing the Future of Power Systems
Smart Grids: Revolutionizing the Future of Power Systems  Automated Power Factor Correction: Improving Energy Efficiency
Automated Power Factor Correction: Improving Energy Efficiency  Powering the Future: A Renewable Energy Harvesting System
Powering the Future: A Renewable Energy Harvesting System  Smart Grid Solutions: Enhancing Electrical Distribution Efficiency
Smart Grid Solutions: Enhancing Electrical Distribution Efficiency 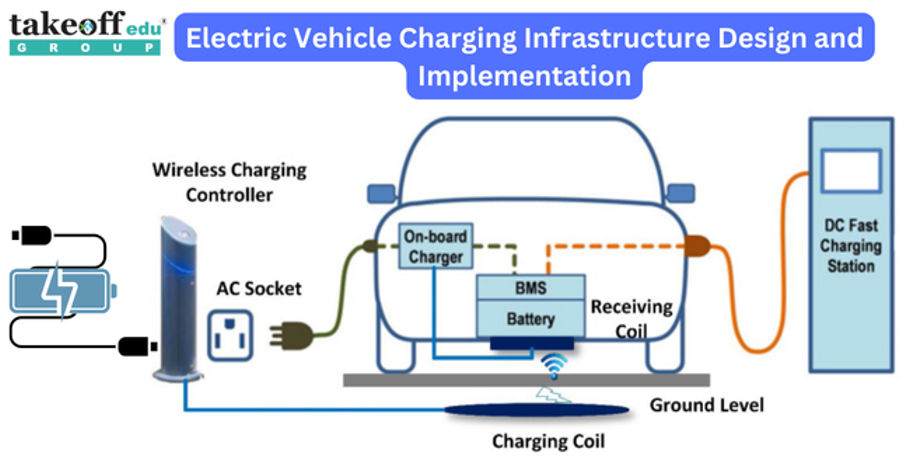 Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Design and Implementation
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Design and Implementation 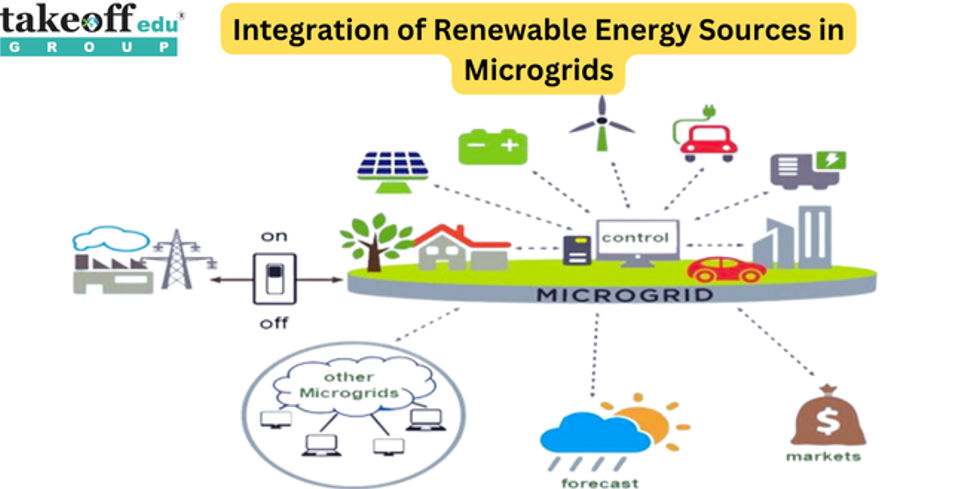 Integration of Renewable Energy Sources in Microgrids
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources in Microgrids  Electrical Projects Engineering Students
Electrical Projects Engineering Students  M.Tech Thermal Engineering Projects
M.Tech Thermal Engineering Projects  IEEE Projects for Electrical Engineering
IEEE Projects for Electrical Engineering  Mini Projects for EEE
Mini Projects for EEE  Mini Projects for Electrical Students
Mini Projects for Electrical Students  Top Electrical Projects for Final Year Students
Top Electrical Projects for Final Year Students  10 Interesting Projects for Electrical Engineering Students 2022
10 Interesting Projects for Electrical Engineering Students 2022  7 Trending Power Systems Based Projects for EEE
7 Trending Power Systems Based Projects for EEE  Top 10 Power Electronics Projects for EEE
Top 10 Power Electronics Projects for EEE  Top 16 Electrical Engineering Projects
Top 16 Electrical Engineering Projects 
 Paper Publishing
Paper Publishing



